The transportation sector is a major contributor to global carbon emissions, prompting a growing need for sustainable alternatives. Green hydrogen, produced through water electrolysis using renewable energy sources, is emerging as a key player in the quest for clean mobility.
Green hydrogen plays a crucial role in decarbonizing transportation as part of a broader strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Hydrogen is considered “green” when it is produced using renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, through a process called electrolysis. This process involves splitting water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) without emitting carbon dioxide.
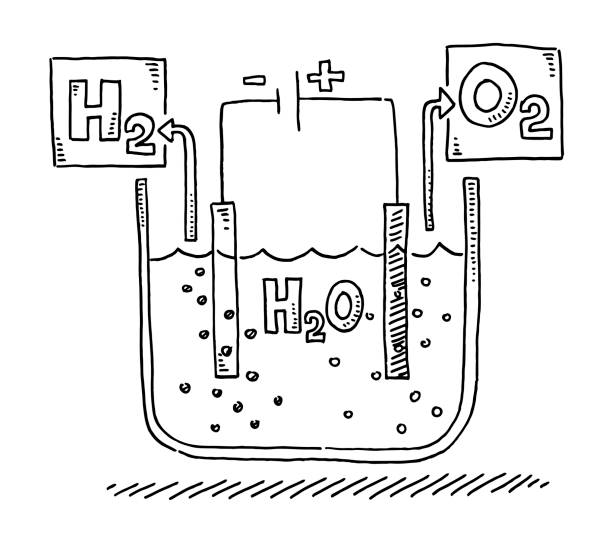
Here’s how electrolysis of water works:
- An electric current is passed through the water.
- The water splits into ions.
- The ions move to opposite electrodes to liberate pure hydrogen and oxygen gases
- The cathode generates hydrogen gas, while the anode generates oxygen gas.
The hydrogen gas can be used as fuel, but it must be kept separate from the oxygen because the mixture is extremely explosive.
Decarbonization is the term used for the reduction of carbon dioxide (CO2) output into the atmosphere.
Here’s how green hydrogen plays a significant role in decarbonizing transportation:
Hydrogen is an energy carrier and fuel that, when fed into a fuel cell, can power vehicles and trucks without releasing harmful emissions. Hydrogen and fuel cells can reduce emissions in heavy-duty vehicles.
Hydrogen can serve as an efficient energy storage medium. Excess renewable energy, which is often generated when demand is low, can be used for electrolysis to produce hydrogen. This hydrogen can then be stored and utilized later to produce electricity or power vehicles when renewable energy generation is insufficient.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) typically have longer driving ranges and quicker refueling times compared to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs). This advantage makes hydrogen-powered vehicles more comparable to conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles, addressing some of the range anxiety concerns associated with BEVs.
Hydrogen can be used in various transportation sectors beyond cars, such as buses, trucks, trains, ships, and aircraft. Its versatility makes it a potential solution for decarbonizing different modes of transportation, contributing to a more comprehensive reduction in greenhouse gas emissions across the transport sector.
Everything in this universe has both positive and negative sides. So, some of the major challenges associated with green hydrogen adoption in transportation are:
The production of green hydrogen remains more expensive compared to hydrogen derived from fossil fuels (grey hydrogen) due to the costs of renewable energy and electrolysis technologies. As renewable energy costs decrease and technology advances, the cost of green hydrogen is expected to decline.
Establishing a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure requires significant investment, including building production facilities and a network of refueling stations. This may initially limit widespread adoption.
Electrolysis, the process used to produce green hydrogen, has energy efficiency limitations. Advancements in electrolysis technologies are needed to improve efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Overall, while green hydrogen holds promise in decarbonizing transportation, continued technological advancements, cost reductions, supportive policies, and infrastructure development are essential to realize its full potential in creating a cleaner and sustainable transportation system.


Collective resonance! Harmonize through sprunkis‘ interconnected audio matrix!
Rhythm interface cartography! Sprunki maps new audio territories through browser magic. The Spunky Game community’s dance challenge phenomena demonstrates crowd-sourced innovation!