.A solar cell or photovoltaic cell (PV cell) is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect.
The photovoltaic effect is the generation of voltage and electric current in a material upon exposure to light.
The PV cell is composed of semiconductor material; the “semi” means that it can conduct electricity better than an insulator but not as well as a good conductor like a metal. There are several different semiconductor materials used in PV cells.
When the semiconductor is exposed to light, it absorbs the light’s energy and transfers it to negatively charged particles in the material called electrons. This extra energy allows the electrons to flow through the material as an electrical current. This current is extracted through conductive metal contacts – the grid-like lines on solar cells – and can then be used to power homes and the rest of the electric grid.

Materials of solar cell
Solar cells are composed of various semiconducting materials:
- Crystalline silicon
- Cadmium telluride
- Copper indium diselenide
- Gallium arsenide
- Indium phosphide
- Zinc sulphide
Over 95% of all the solar cells produced worldwide are composed of semiconductor material Silicon (Si). The availability of silicon is a very big advantage as it is the second most abundant element in the earth’s crust.
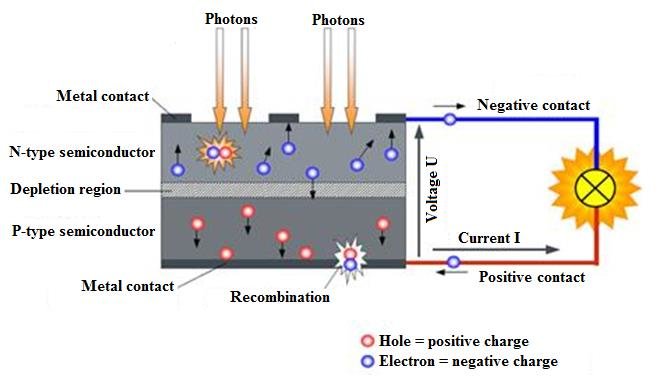
To produce a solar cell the semiconductor is doped. Doping is the intentional introduction of chemical elements into the semiconductor to modulate its electrical, optical, and structural properties. Depending upon doping; one can obtain a surplus of either positive charge carriers known as the p-conducting semiconductor layer or negative charge carriers known as the n-conducting semiconductor layer.
When two differently contaminated semiconductor layers (p-type, and n-type) are combined, they are called p-n junction results on the boundary of the layers.
The generation of voltage across the PN junction in a semiconductor due to the absorption of light radiation is called the photovoltaic effect. The device based on this effect is called a Photovoltaic device.
Photovoltaic energy conversion relies on the number of photons struck on the earth. On a clear day about 4.4 x 1017 photos strike a square centimeter on Earth’s every second. Only some of these photons those with energy over the band gap can be converted into electricity by the solar cell.

