Solar energy is one of the cleanest and most abundant renewable energy sources available. The sun emits energy in the form of light and heat, which can be harnessed through various technologies to generate electricity, provide light, and heat water and space.
Solar energy is the radiation from the sun capable of producing heat, causing chemical reactions, or generating electricity. The total amount of solar energy received on Earth exceeds the world’s current and anticipated energy needs, making it an up-and-coming resource for the future. Solar energy is sustainable and inexhaustible, unlike fossil fuels, which are finite and environmentally damaging.
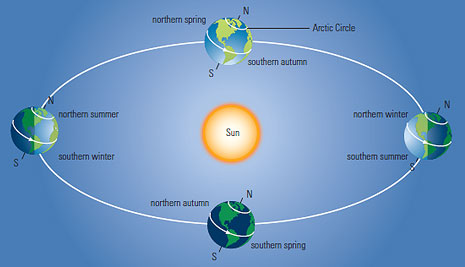
Earth’s elliptical orbit around the sun (1 revolution per year) is quasi-circular. The distance to the sun varies to a small extent.
Quasicircular means almost circular, but not quite. The word "quasi" comes from the Latin word quasi, which means "almost, as it were".
Earth’s tilt angle of 23.4° is the cause of the seasons. When the Earth’s axis points towards the sun, it is summer for that hemisphere. The summer solstice occurs when the sun is directly over the Tropic of Cancer near June 21st.
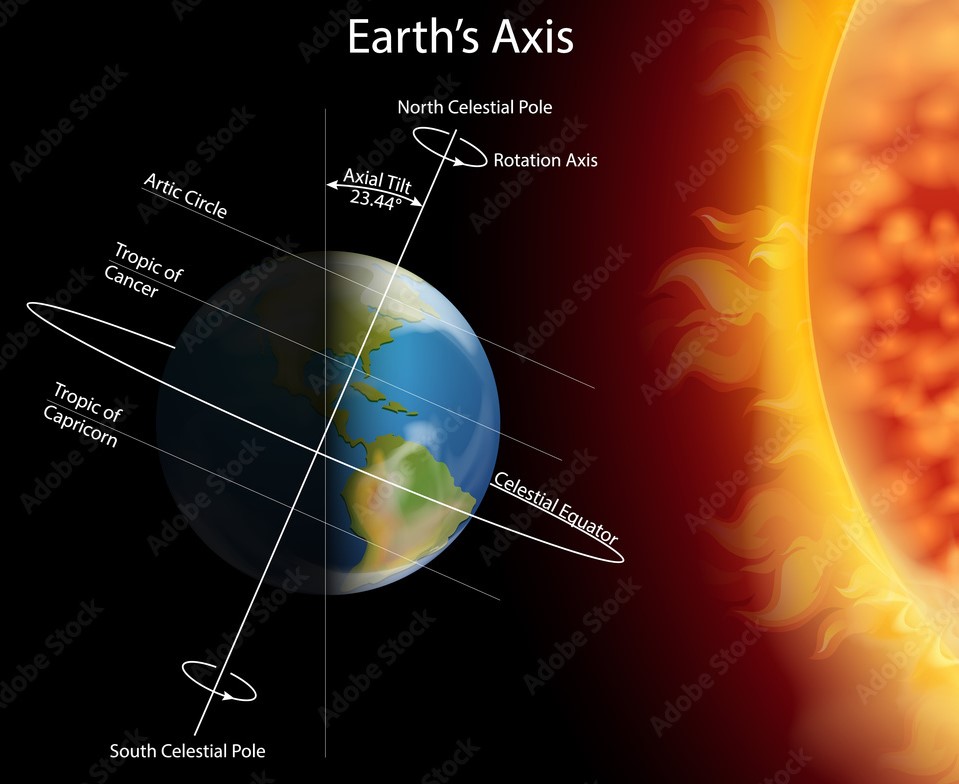
For example: When the North Pole is tilted towards the sun; it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere; during that time earth receives more irradiation daily (kWh per square meter per day). During winter it’s the southern hemisphere which is tilted towards the sun. In summer we have more hours of sun (which is then visible or not so visible, depending on the presence of clouds) and the sun goes up higher in the sky, resulting in higher temperatures.
Solar irradiance is a measure of the sun's intensity or power density over a certain area, commonly defined as being an average intensity of 1kW/m2
How is Solar Energy Captured?
Solar energy is captured through several technologies, primarily photovoltaic (PV) panels and solar thermal systems. These technologies convert sunlight into usable forms of energy such as electricity and heat.
Photovoltaic (PV) Panels: These panels contain solar cells made of semiconductor materials (like silicon) that convert sunlight directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it knocks electrons loose from their atoms, allowing the electrons to flow through the material to produce electricity.
Solar Thermal Systems: These systems capture the sun’s heat. This heat can be used directly for heating spaces or water (solar heating systems) or to produce steam for generating electricity in solar power plants (concentrated solar power, or CSP).
Conversion of Solar Energy.
The conversion of solar energy into electricity or heat involves different processes depending on the technology:
Direct Conversion: PV panels convert sunlight directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. The efficiency of this conversion depends on the materials used in the solar cells, the design of the solar panel, and the intensity of the sunlight.
Indirect Conversion: Solar thermal systems use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver that heats a fluid. This heat can then be used directly or converted into mechanical energy to drive a generator that produces electricity.
The benefits of solar energy include its abundance, sustainability, and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. It can also reduce electricity bills and increase energy independence. However, challenges remain, such as the variability of sunlight, the initial costs of solar technology, and the need for energy storage solutions to provide power when sunlight is not available.

